CentOS 7定时执行python脚本
CentOS 7定时执行python脚本
在CentOS下,可以使用crontab进行定时任务的处理。
一、crontab的安装
默认情况下,CentOS 7中已经安装有crontab,如果没有安装,可以通过yum进行安装。
yum install crontabs
二、crontab的定时语法说明
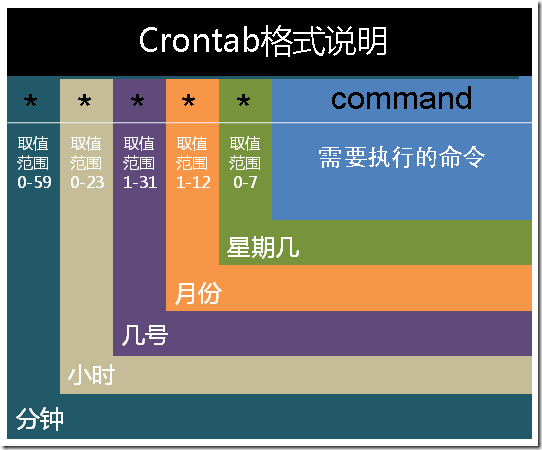
corntab中,一行代码就是一个定时任务,其语法结构可以通过这个图来理解。
| 字符 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| * | 代表取值范围内的所有 |
| / | 代表”每” |
| – | 代表从某个数字到某个数字 |
| , | 代表离散的取值(取值的列表) |
一些常用的时间写法
| 表达式 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| * * * * * | 每分钟执行 |
| * */4 * * * | 每4小时执行 |
| 0 4 * * * | 每天4点执行 |
| 0 12 */2 * * | 每2天执行一次,在12点0分开始运行 |
| * * * * 0 | 每周日执行 |
| * * * * 6,0 | 每周六、日执行 |
| 5 * * * * | 每小时的第5分钟执行 |
三、设置定时任务
编写python脚本
# test.py
print("hello world!")
通过Finalshell上传到指定目录下
修改配置文件
[root@VM_0_8_centos script_py]# whereis crontab
crontab: /usr/bin/crontab /etc/crontab
[root@VM_0_8_centos script_py]# vim /etc/crontab
# 文件末尾添加
* * * * * root /usr/bin/python3 /data/script_py/test.py > test.log
# 每分钟 root身份执行 使用python3 运行 test.py 输出到 test.log
重启服务
systemctl restart crond
查看日志
[root@VM_0_8_centos script_py]# cat /root/test.log
hello world!
注意!
非常重要的一点是要用绝对路径写到命令,否则定时运行失败。因此我们需要先弄清楚python的具体路径。
# 查看系统默认安装的python2的路径
[root@VM_0_8_centos ~]# which python
/usr/bin/python
# 查看自行安装的python3的路径
[root@VM_0_8_centos ~]# which python3
/usr/bin/python3

![CentOS 7定时执行python脚本[Python基础]](https://www.zixueka.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/1696831943-fac0d8d3b222aea.jpg)
